Experiment Name: Determination of Coefficient of Discharge of Flow Measuring Devices.
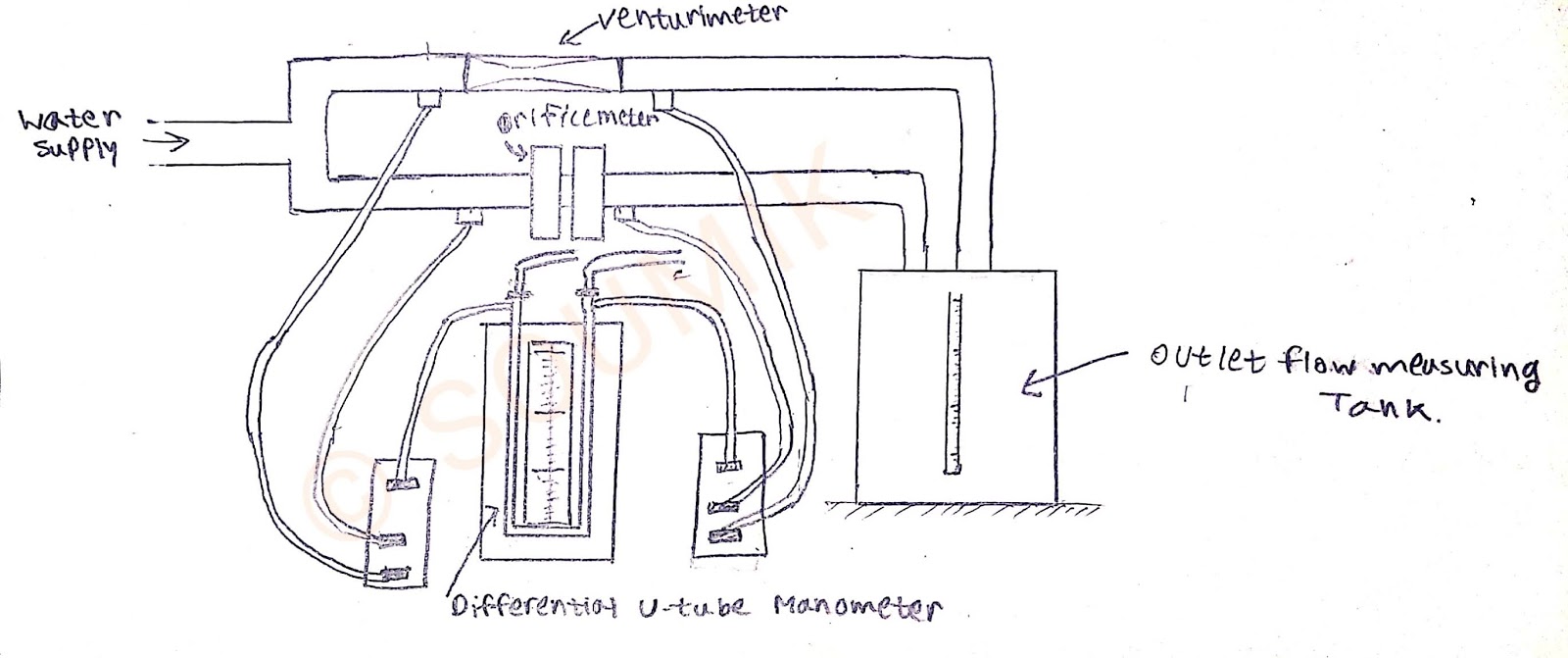
Figure:- Orifice metre(At back with orifice plate) and Venturi metre(At front with converging and diverging shape).
Objective:
(i) To determine the coefficient of discharge of Venturimeter.
(ii) To determine the coefficient of discharge of Orificemeter.
Apparatus Used:
Venturimeter with pipe line assembly, Orificemeter with pipe line assembly, differential U-tube manometer, Flow Measuring Tank and Stop watch.
Theory:
The discharge Q through the flow meter fitted in a pipeline can be expressed in terms of discharge coefficient Cd of the meter and piezometric head difference H across the meter as follows,
Di =Pipe diameter.
Do =Throat diameter for Venturimeter, Orifice diameter for Orificemeter.
Ao=Throat area / Orifice area
H = Piezometric head difference between inlet and throat = x(ρm/ρw−1)
where x = deflection of manometric fluid in differential U tube manometer.
Experimental procedure:
1. Check the manometer connection and if air is tapped in drive out by opening air cock.
2. Check the valves connection to the setup.
3. Open the inlet valve and the flow control valve of the corresponding flow meter pipe line, keeping other inlet valve close.
4. At a particular opening of the flow control valve, take the manometer reading.
5. Measure the flow rate by the volumetric tank and stop watch.
6. Change the flow control valve opening.
7. Repeat the steps 4, 5 & 6 to take different reading.
8. After Venturi metre reading repeat the same proceedure for Orifice metre.
Observations:(Sample reading shown below)
- Specific gravity of the manometric fluid= 13.633
- Cross sectional area of the volumetric tank 300 mm × 300 mm
- Temperature of the water= 20°C
- Density of the water= 998.2 kg/m³
- Viscosity of the water from standard chart= 8.90×10⁻⁴ Pa.s
Parameter Table:
FAQ:
1. List the sources of the errors of the experiment.
a. when all valve is closed in beginning manometric fluid difference is not zero.
b. The parallax error should be avoided.
c. Maintain a constant discharge during each reading.
d. Keep the other closed during one experiment to prevent leakage.
e. The pipe connection should be dust,dirt free to get proper reading of coefficient of discharge of flow metre.
2. Provide sample calculation.
3. Define co-efficient of discharge for Orificemeter and discuss “Vena-contracta”.
Coefficient of discharge can be defined as the ratio between actual flow of the discharge to the theoretical discharge.
When fluid is passing through a small orifice /hole , sudden contraction is taking place in the stream of fluid. Once the fluid is passing through the orifice even though the contraction of the stream remains continue in the streamwise direction. The minimum flow cross section of the stream is called the point of venacontracta, where velocity is maximum.
4. Draw the schematic diagram of the setup.
5. Compare the use of Orificemeter and Venturimeter as primary elements for flow measurement.
1. A venturi meter can be used to measure flow rate of all incompressible fluids (gases with low pressure variations, as wells as liquids), whereas an orifice meter is generally used for measuring the flow rate of liquid.
2. Venturimeter gives you a better result than Orificemeter as Venturi meter losses are less so coefficient of discharge is higher whereas in orifice meter due to no convergent and divergent cones there are more losses and hence its coefficient of discharge is less.
3. Venturimeters are relatively expensive than orifice.The installation cost is high but lower maintenance and operational cost.
Written by- SOUMIK.